Fiber optic cables have transformed data transmission worldwide. They boast many amazing features. These include high bandwidth, minimal loss, and resistance to electromagnetic disturbance. Composed of thin glass or plastic elements called optical fibers that transmit data as light pulses, fiber cables involve two fundamental sorts – single-mode and multimode fiber. Let’s examine both fiber optic cable types.
What Are the Differences?
Many key aspects differentiate these two optic fiber cable solutions. These include:
- Core Diameter
The core diameter is the primary distinction between these optical fiber cable types. Single-mode has an extremely thin core that is only 5-10 micrometers wide. Multimode has a much wider core that is either 50 or 62.5 micrometers across.
- Dispersion
Dispersion is much less pronounced in single-mode fiber optic cable in relation to multimode fiber, underscoring its advantages for applications demanding minimal signal degradation over long distances. This is because its single core limits the light to just one path.
- Bandwidth
Single-mode fiber delivers significantly higher bandwidth potential (up to 100,000 GHZ, theoretically limitless) that persists admirably over extended transmission lengths. It can convey data at full line rate over fiber cable distance ranges exceeding tens of kilometers. In contrast, the bandwidth of multimode fiber optic cable (up to 28000MHz*km) deteriorates noticeably beyond short reaches, reducing the effective data rate as multimode fiber distance grows.
- Transmission Range
The purity of transmission through the single light mode allows the single-mode fiber to support connectivity up to 100 kilometers or more, limited primarily by intrinsic fiber losses. Multimode fiber, on the other hand, encounters greater distortions, which confine its usable transmission range to about 550m-2 km at most before signal quality degradation becomes unacceptable.
- Color
For easy distinguishability during installation, single-mode fiber optic cable solutions are most commonly constructed with yellow jackets, while multimode variants usually employ an orange sheathing. These standard pigmentations help technicians quickly identify the appropriate fiber type from a visual inspection.
Comparison Highlights
The following comparison table highlights the differences between single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables:
Parameter/Characteristic | Single-Mode Fiber | Multimode Fiber |
Core Diameter | 5-10 μm | 50 or 62.5 μm |
Dispersion | Low dispersion | Higher dispersion |
Bandwidth | High bandwidth (up to 100,000 GHz, theoretically limitless) | Lower fiber optic cable bandwidth (up to 28000MHz*km) |
Transmission Range | Up to 100 km or more | Up to 550m-2 km |
Color | Most commonly yellow jacket | Standard orange jacket |
Applications | Long haul connections between cities/countries | Shorter campus/building links |
Drawbacks | Small core size increases costs/complexity | Greater dispersion limits maximum speeds |
Choose Based on Application
The optimal fiber optic cable type depends on the application, i.e., data transmission needs. Multimode fiber generally supports shorter campus or building networks with its cost-effectiveness and easiness of use. However, for longer-distance applications such as connecting cities or countries, the low-loss properties of single-mode fiber are better suited to provide bandwidth over tens of kilometers. Factors like installation environment, network topology, projected growth, and bandwidth requirements need assessing to determine the most optimal choice.
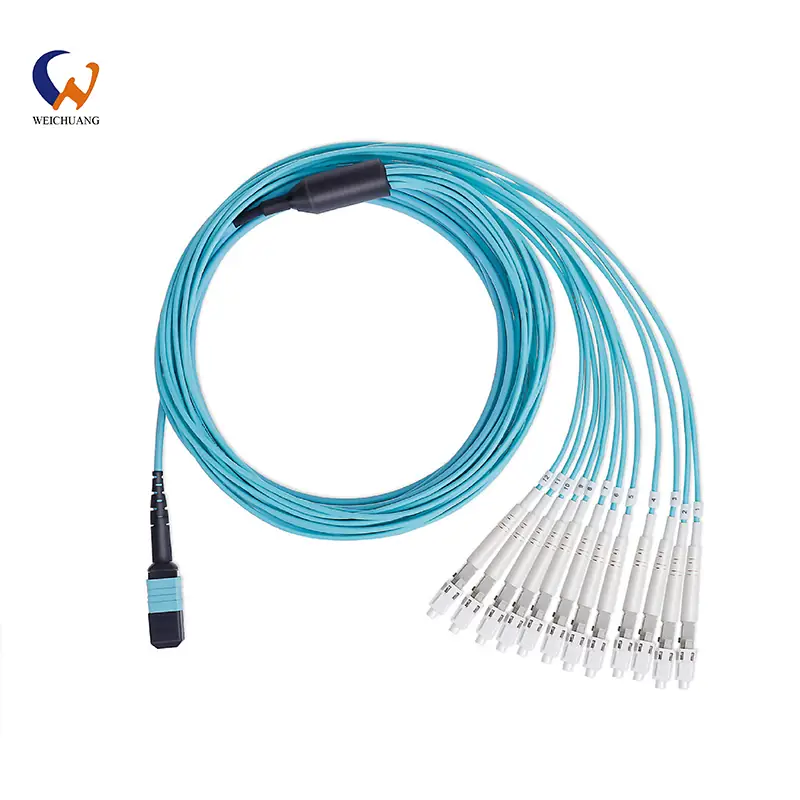
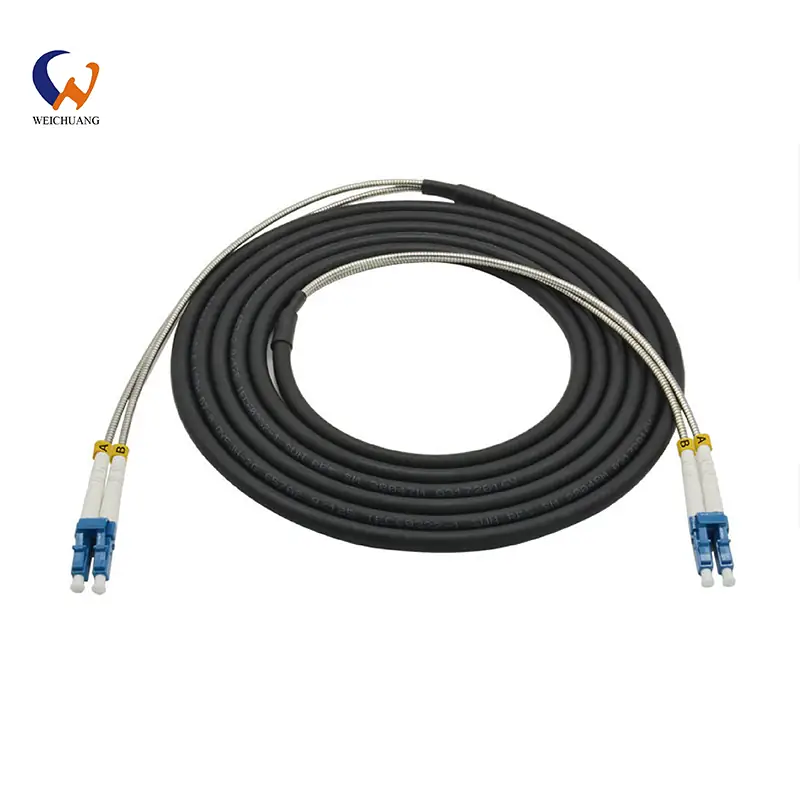
Product Highlight: MPO/MTP Trunks Outdoor Cable
The seasoned brand Weichuang Optics manufactures a variety of high-quality fiber optic cables to meet all application needs. As a leading fiber optic cable manufacturer located in China, we have years of industry experience and employ modern facilities along with stringent ISO quality controls.
The MPO/MTP Trunks Outdoor Cable is one of our top-selling products. Available from 12 to 144 fiber cores using MPO connectors, it reduces failure points and simplifies installation. It supports bandwidths up to 100G to meet growing demands and features a protective jacket engineered for durability through all weather. The small, flexible design and minimum bending radius ease storage and handling. Tough protective jacket withstands bending during outdoor deployment and harsh conditions.
Conclusion
Overall, there are several key differences between single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables. Each type has distinct characteristics, making it preferable for long-haul or short-haul use cases respectively. As network needs continue growing, carefully assessing each project’s bandwidth demands, topology, and budget is key to choosing the right fiber solution. Innovative products from manufacturers like Weichuang Optic aim to simplify deployment processes and maximize performance capabilities. Our robust and versatile MPO/MTP Trunks Outdoor Cable serves as an illustration of this. Visit our website to learn more about it and browse our other offerings.